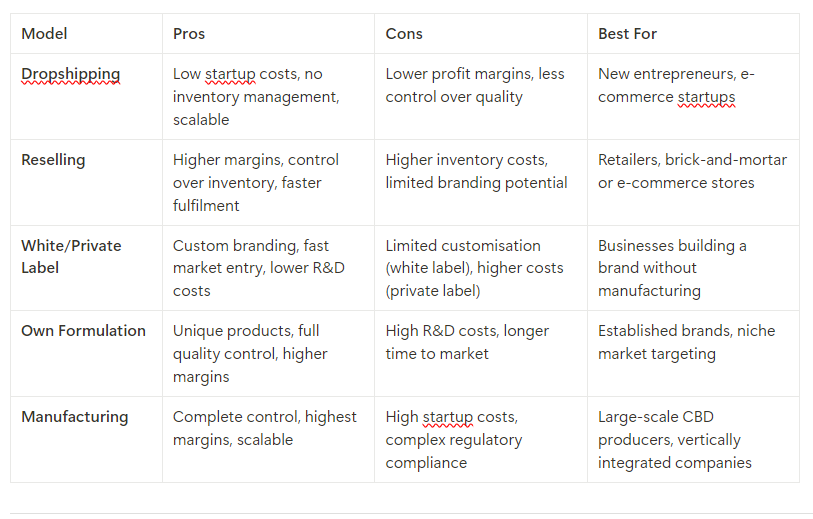
Entering the CBD market involves strategic decisions about how to source, produce, and distribute your products. Whether you're just starting out or looking to expand your offerings, there are several key business models to consider: Dropshipping, Reselling, White/Private Label, Own Formulation, and Manufacturing.
Each approach has its own set of advantages and disadvantages that can impact your startup costs, scalability, branding, and profit margins.
1. Dropshipping
1.1. What Is Dropshipping?
Dropshipping is a retail fulfilment method where you sell products through your website or marketplace, but the products are shipped directly from the supplier to the customer. You don't handle the physical products yourself—your job is to market the products and process orders, while the dropshipping partner manages inventory and fulfilment.
1.2. Pros of Dropshipping:
Low Startup Costs: You don’t need to purchase inventory upfront, reducing the initial capital investment.
No Inventory Management: The supplier handles storage, packaging, and shipping, freeing you from logistical headaches.
Scalability: Since you’re not responsible for warehousing or shipping, scaling the business is easier.
1.3. Cons of Dropshipping:
Lower Profit Margins: Since you’re paying the supplier to fulfil orders, your profit margins will typically be lower than other models.
Less Control Over Quality: You rely on the supplier to ensure product quality and timely fulfilment, which can lead to issues if their standards aren’t met.
Limited Customisation: Dropshipping partners usually offer standard products with limited or no branding options, making it harder to differentiate your brand.
1.4. Best Use Case:
Dropshipping is ideal for entrepreneurs who want to test the CBD market with minimal risk or for those focusing on building an e-commerce brand without investing in inventory and logistics.
2. Reselling
2.1. What Is Reselling?
Reselling involves purchasing CBD products from manufacturers or wholesalers and selling them at a markup. Unlike dropshipping, you handle the inventory and fulfilment yourself, which gives you more control over the product flow.
2.2. Pros of Reselling:
Higher Profit Margins: By purchasing wholesale, you can set your own prices and potentially achieve better margins compared to dropshipping.
Control Over Inventory: You manage your stock, allowing you to verify product quality and ship orders quickly.
Established Products: Reselling established CBD brands can give you credibility and attract customers looking for trusted products.
2.3. Cons of Reselling:
Inventory Costs: You need to purchase inventory upfront, which increases initial capital requirements.
Storage and Shipping: Managing your own fulfilment means you’ll need space to store products and the infrastructure to handle shipping and returns.
Limited Branding: Since you're selling existing brands, it’s harder to build a unique identity for your business.
2.4. Best Use Case:
Reselling is suitable for businesses that want more control over product quality and inventory without the complexity of developing their own formulations. It’s also a good fit for brick-and-mortar stores or e-commerce platforms looking to stock trusted CBD products.
3. White Label/Private Label
3.1. What Is White Label and Private Label?
White label and private label CBD products are manufactured by a third party but branded under your company’s name. In white label arrangements, the products are standardised and sold to multiple companies, while private label allows for more customisation in product formulation and branding.
3.2. Pros of White/Private Label:
Custom Branding: You can build a unique brand identity by applying your own labels, logos, and packaging to products.
Faster to Market: Since the product formulations are pre-made, white and private label products allow you to enter the market quickly.
Lower R&D Costs: You don’t need to invest in research and development, as the manufacturer handles product formulation.
3.3. Cons of White/Private Label:
Limited Customisation (White Label): With white label products, customisation options are often minimal, limiting your ability to differentiate your product from others selling the same formula.
Higher Costs (Private Label): Custom private label products usually require higher minimum order quantities and more investment in branding and packaging.
Dependent on Manufacturer: You rely heavily on the manufacturer for product quality, supply chain management, and compliance with regulations.
3.4. Best Use Case:
White and private label options are ideal for businesses that want to build their own brand without the complexities of manufacturing. This model suits entrepreneurs looking for a relatively quick market entry with full control over branding and packaging.
4. Own Formulation
4.1. What Is Own Formulation?
Own formulation involves working with a manufacturer or lab to develop a unique CBD product from scratch. You control the entire product development process, including the choice of ingredients, potency, flavour, and delivery methods (e.g., oils, capsules, topicals).
4.2. Pros of Own Formulation:
Unique Products: You can create bespoke products tailored to your target audience, offering a unique selling proposition (USP).
Full Control Over Quality: You choose the ingredients and oversee the formulation process, ensuring the product meets your quality standards.
Higher Profit Margins: Since you own the formulation, you can set your pricing and build a high-end brand with premium margins.
4.3. Cons of Own Formulation:
Higher R&D Costs: Developing a product from scratch involves significant investment in research, development, and testing, including stability studies and safety assessments.
Longer Time to Market: The formulation and testing process takes time, delaying your product launch compared to white or private label options.
Regulatory Hurdles: You must ensure your formulation complies with UK regulations, such as Novel Foods authorisation, which can be costly and time-consuming.
4.4. Best Use Case:
Own formulation is perfect for established brands looking to innovate in the CBD space or entrepreneurs targeting a niche market with highly specific product demands. It’s also a good option for those who want complete control over their product’s ingredients and quality.
5. Manufacturing
5.1. What Is Manufacturing?
Manufacturing your own CBD products involves building or outsourcing a facility to extract and produce CBD from raw cannabis or hemp plants. This gives you full control over the entire process, from cultivation to final product packaging.
5.2. Pros of Manufacturing:
Complete Control Over Production: You manage the entire supply chain, ensuring consistent product quality, purity, and compliance with regulations.
Higher Profit Margins: Since you control the production process, you can potentially achieve higher profit margins by cutting out third-party suppliers or manufacturers.
Scalability: Owning the manufacturing process allows you to scale your operations and meet increasing demand without relying on external suppliers.
5.3. Cons of Manufacturing:
High Startup Costs: Manufacturing requires significant investment in equipment, facilities, and staffing, as well as compliance with strict health and safety regulations.
Complex Regulatory Compliance: You must adhere to multiple regulations, including Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), health and safety, and environmental standards, which can add complexity to your operations.
Operational Challenges: Managing a manufacturing facility involves logistical, operational, and supply chain management, which requires expertise and ongoing oversight.
5.4. Best Use Case:
Manufacturing is best suited for established companies with the resources to invest in production facilities or large-scale CBD businesses looking to control every aspect of the supply chain for quality assurance and cost control.
Comparison of Market Entry Models