The extraction method used to obtain CBD from the cannabis or hemp plant significantly impacts the quality, purity, and overall effectiveness of the final product. Choosing the right extraction method is essential for producing high-quality CBD that complies with legal and safety regulations. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages in terms of efficiency, cost, and the types of compounds retained in the final extract.
1. CO₂ Extraction
1.1. What Is CO₂ Extraction?
CO₂ (carbon dioxide) extraction is one of the most popular and widely used methods for extracting CBD from cannabis or hemp plants. It involves using pressurised carbon dioxide to pull cannabinoids, terpenes, and other compounds from the plant material. This method is considered supercritical when the CO₂ is heated and pressurised to a point where it behaves as both a gas and a liquid, allowing it to dissolve compounds more efficiently.
1.2. Process:
Supercritical CO₂ is passed through plant material in an extraction chamber.
The CO₂ acts as a solvent to separate the cannabinoids, terpenes, and other beneficial compounds from the plant.
The extracted material is then collected, and the CO₂ is removed by reducing the pressure, leaving behind the pure extract.
1.3. Advantages of CO₂ Extraction:
High Purity: CO₂ extraction produces some of the purest and highest-quality CBD extracts, as it preserves cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids without using harsh chemicals.
Clean and Safe: CO₂ is a natural, non-toxic solvent, so there are no harmful residues left behind in the final product.
Customisable: Supercritical CO₂ extraction allows for precise control over temperature and pressure, enabling producers to customise the extraction process and isolate specific compounds like cannabinoids and terpenes.
1.4. Disadvantages:
Cost: CO₂ extraction requires expensive equipment and a high level of technical expertise, which can make it a costly option, especially for small-scale operations.
1.5. Best Use Cases:
CO₂ extraction is ideal for producing full-spectrum or broad-spectrum CBD products, as it allows for the retention of multiple cannabinoids and terpenes, creating a high-quality extract that maximises the entourage effect.
2. Solvent Extraction (Ethanol or Hydrocarbon)
2.1. What Is Solvent Extraction?
In solvent extraction, a liquid solvent such as ethanol or hydrocarbons (e.g., butane, propane) is used to dissolve and extract the desired compounds from the plant material. This method is faster and less expensive than CO₂ extraction but involves the use of chemicals, which may affect the final product's purity.
2.2. Process:
Plant material is soaked in a solvent (usually ethanol, but butane or propane can also be used).
The solvent dissolves the cannabinoids, terpenes, and other plant compounds.
The solution is then evaporated to remove the solvent, leaving behind the concentrated extract.
2.3. Types of Solvent Extraction:
Ethanol Extraction: Ethanol is widely considered safer and less toxic than hydrocarbons, and it can be used in cold or warm extraction processes.
Hydrocarbon Extraction: Butane and propane are sometimes used to extract cannabinoids because they are efficient solvents. However, they are more volatile and can leave behind residues if not handled correctly.
2.4. Advantages of Solvent Extraction:
Efficiency: Solvent extraction is fast and relatively inexpensive compared to CO₂ extraction, making it a good option for large-scale production.
High Cannabinoid Content: Solvent extraction can yield high levels of cannabinoids, especially when using ethanol or hydrocarbons, making it effective for creating concentrates or distillates.
2.5. Disadvantages:
Solvent Residues: Solvent extraction methods, particularly those using hydrocarbons, can leave behind chemical residues if not properly evaporated. This can lower the quality and safety of the final product.
Potential for Impurities: The extraction process can also extract undesirable compounds like chlorophyll, which can affect the taste and quality of the product.
2.6. Best Use Cases:
Ethanol extraction is ideal for CBD isolates and broad-spectrum products, as it is an effective and cost-efficient method for extracting high concentrations of CBD. Hydrocarbon extraction, while riskier, is often used for making potent concentrates like CBD wax or shatter.
3. Lipid-Based Extraction
3.1. What Is Lipid Extraction?
Lipid-based extraction involves using natural fats or oils, such as coconut oil or MCT oil, to extract cannabinoids from the plant. This method is solvent-free and uses the fat molecules in the oil to bind with the cannabinoids, creating a CBD-infused oil.
3.2. Process:
The hemp or cannabis plant material is heated to decarboxylate the cannabinoids.
The decarboxylated plant material is then mixed with the carrier oil and heated slowly to allow the cannabinoids to bind to the oil.
The resulting mixture is filtered to remove plant material, leaving a CBD-infused oil.
3.3. Advantages of Lipid Extraction:
Chemical-Free: Lipid extraction does not involve the use of solvents or chemicals, making it a natural and safe method.
Cost-Effective: This method is low-cost and can be easily performed without expensive equipment, making it ideal for smaller producers or DIY extraction.
3.4. Disadvantages:
Lower Concentration: Lipid extraction generally results in a less concentrated CBD extract compared to CO₂ or solvent-based methods, making it less suitable for high-potency products.
Shorter Shelf Life: The presence of fats in the final product can lead to a shorter shelf life compared to other extraction methods.
3.5. Best Use Cases:
Lipid-based extraction is ideal for creating infused oils, topicals, and edibles, where a lower concentration of CBD is acceptable and a natural, solvent-free process is preferred.
4. Steam Distillation
4.1. What Is Steam Distillation?
Steam distillation is a traditional method of extracting essential oils and can be used to extract cannabinoids and terpenes from cannabis or hemp. The process involves using steam to separate the cannabinoids from the plant material.
4.2. Process:
Steam is passed through the plant material, causing the cannabinoids and other compounds to vaporise.
The vapour is collected and condensed into a liquid, where the cannabinoids and terpenes can be separated from the water.
4.3. Advantages of Steam Distillation:
Natural Method: Like lipid extraction, steam distillation does not involve chemical solvents, making it a clean and natural method.
Terpene Retention: This method is particularly effective at retaining the terpenes, making it suitable for products where aroma and flavour are important.
4.4. Disadvantages:
Less Efficient: Steam distillation is not as efficient as other methods and can result in lower yields of cannabinoids, especially CBD.
Temperature Sensitivity: Cannabinoids and terpenes can degrade at the high temperatures required for steam distillation, affecting the potency and quality of the final product.
4.5. Best Use Cases:
Steam distillation is best for products that focus on aromatherapy or terpene-rich formulations, such as essential oil blends or topical CBD products.
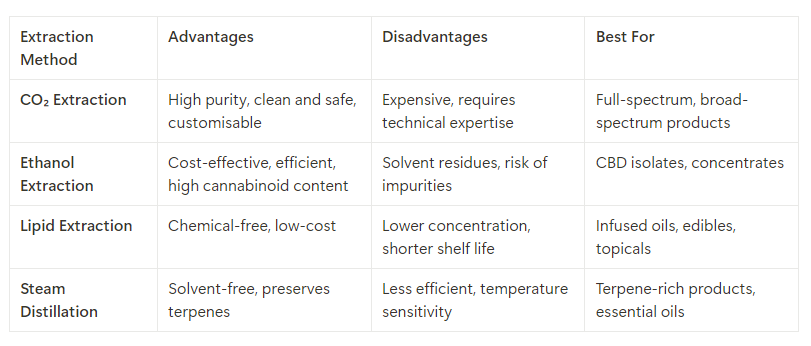
5. Comparing Extraction Methods: Which Is Right for Your Business?
Choosing the right extraction method depends on several factors, including product type, target market, and production scale. Here’s a summary to help you decide:
6. Regulatory Considerations for Extraction
Regardless of the extraction method you choose, it is essential to comply with UK regulations:
- THC Limits: All CBD products must contain less than 1mg of THC per product.
- Testing: Regular testing for cannabinoid content and solvent residues (if applicable) is required to ensure product safety and compliance.
- Labelling: Transparency in product labelling, including the extraction method used, can help build consumer trust and meet regulatory standards.






